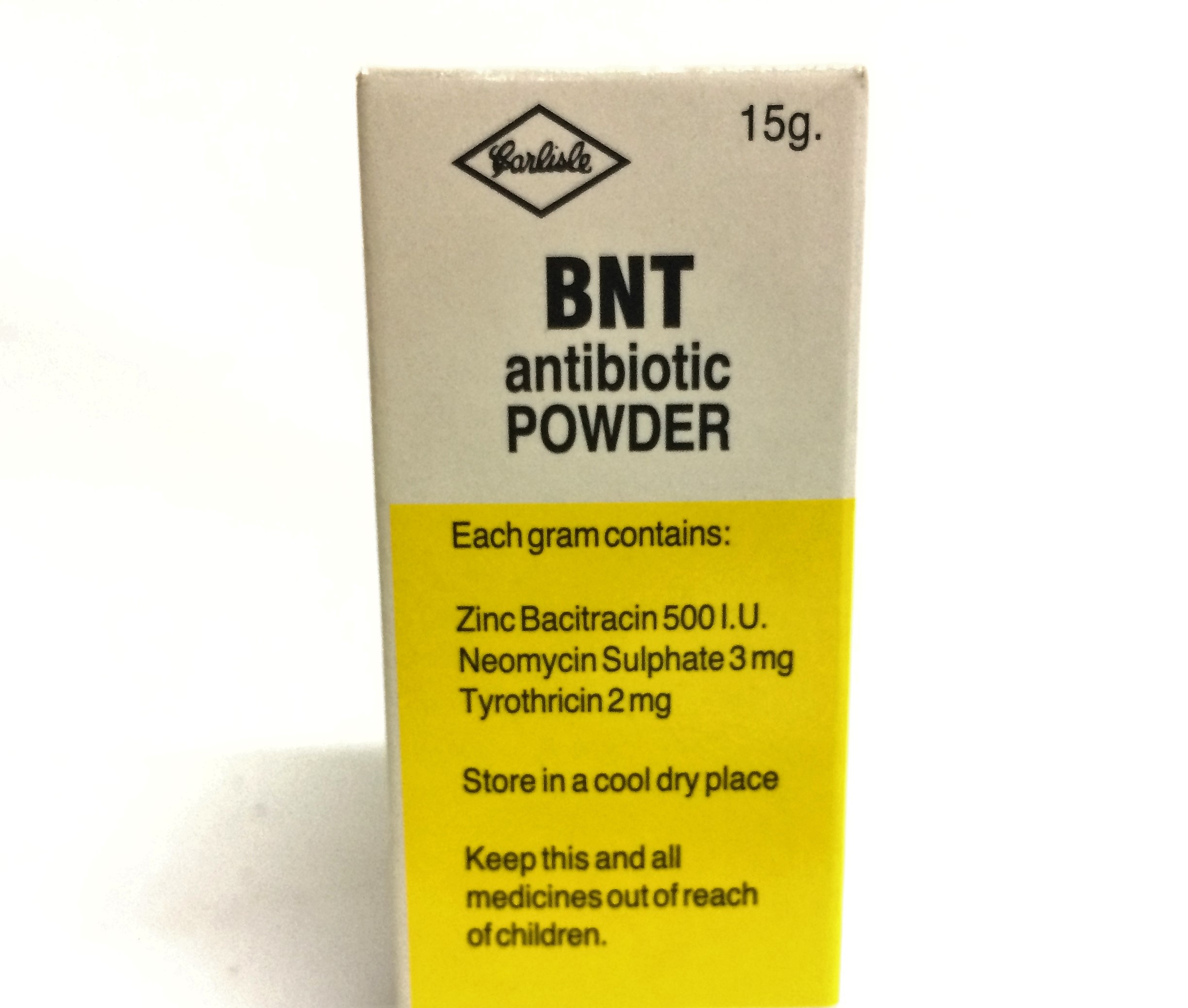
BNT ANTIBIOTIC POWDER
$35.00
BNT Powder:
For treatment of a wide antibacterial spectrum.
Out of stock
By combining three quick-acting highly potent antibiotics, a wide antibacterial spectrum has been made available in ‘BNT’.
BACITRACIN: Obtained from a strain of B. subtilis, having a range of
activity similar to that of penicillin, will inhibit the growth of streptococci,
staphylococci, gonococci, meningococci, clostridia, 7. pallidum and E.
histolytica and its effect is not altered by serum, pus, or necrotic tissue.
Bacitracin may be applied topically or injected into such pyogenic lesions
(caused by susceptible organisms) as furuncles, carbuncles, ulcers, felons,
paronychia and pyodermatoses.
NEOMYCIN: Derived from -a- strain. of streptomycetes closely
related to Streptomyces fradiae is a polybasic compound; heat-stable and is
resistant to the action of acid (pH2) at the temperature of boiling water. It is
bactericidal in vitro against a wide variety of both gram-negative and
gram-positive organisms. There is some indication that it is the most effective
agent in the treatment of infections due to P. vulgaris. Applied topically the
drug is well tolerated and rarely produces allergic manifestations.
TYROTHRICIN: Is an extract obtained from B. brevis and consisting
principally of gramicidin and tyrocidin, when applied locally it is of value in
treating superficial ulcers, draining abscesses, empyema and pyodermatoses
due to gram-positive organisms such as staphylococci and pneumococci.
The antibiotics in ‘BNT’ are seldom used systemically and hence less
likely to cause a cross resistance being developed by organisms to other
antibiotics, yet they provide effective therapy against many pathogenic
organisms with virtually no danger of unfavourable side effects.
Indications: Certain types of superficial bacterial skin infections and
ulcers, carbuncles, furunculosis, impetigo and abscesses.
Administration: ‘BNT’ should be applied to the infected area two or three
times daily for best results.
| Weight | 0.1 lbs |
|---|
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.